

For this reason, RNN’s are more effective.
WHAT DOES TRANSFORMER EN MEAN IN FRENCH SERIES
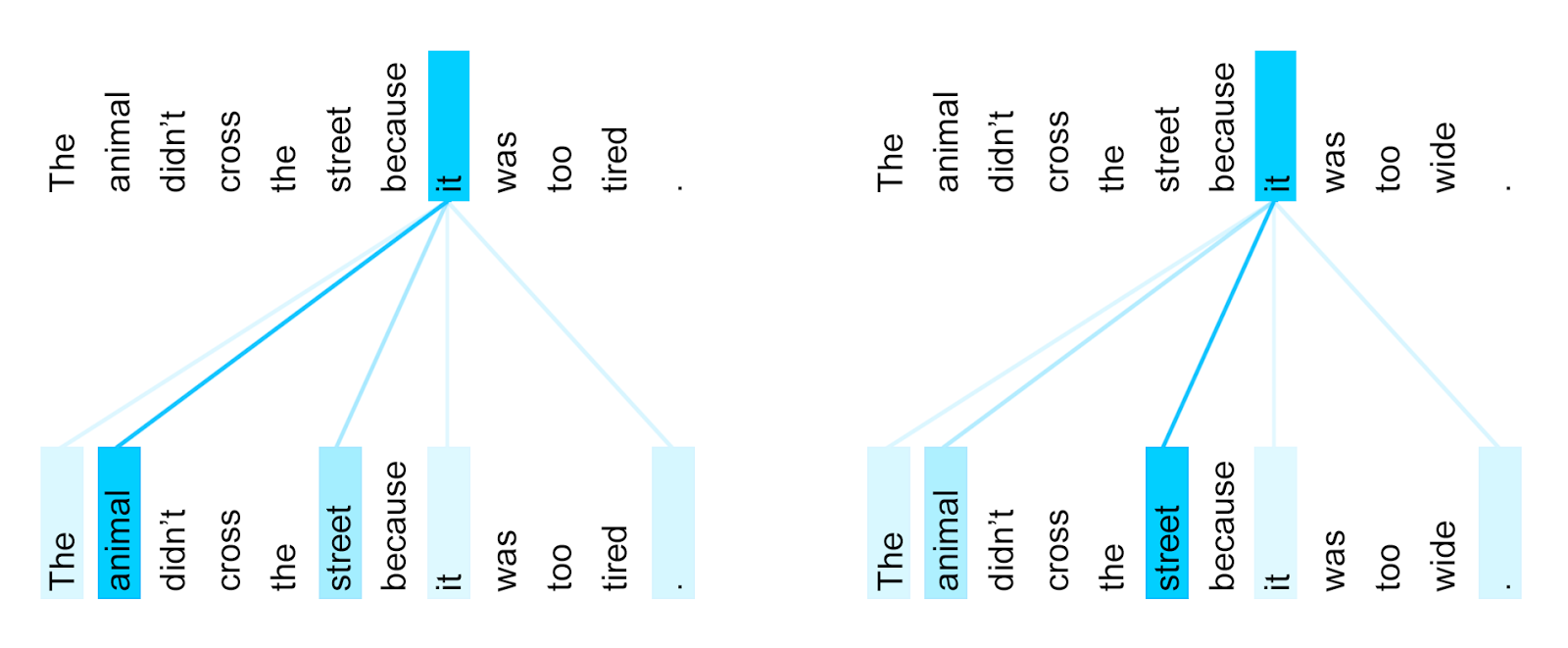
Language cannot be thought of as a series of isolated words laid out in sequential order, but rather a series of interrelational words that are constantly interacting with each other throughout the sentence, paragraph, and whole text. The response to this neural net pitfall is the creation of the recurrent neural network, or RNN. Pictured is a visual representation of a neural network, in our case “input” would be books/text, the “hidden layer” would be where the model learns the relationships between words, and the “output” our desired outcome, such as a translation of the input text. Neural networks struggle to understand the relationships of sequential words and phrases even if supplied with ample training data. This is because the words that make up language aren’t independent from each other a series of words can take on new meaning with the addition or subtraction of other words which makes the process of understanding text much more complex. Just feed the neural net a few classic texts from Shakespeare, Twain, Woolf and Douglas Adams, for good measure, and it will be able to understand human language in no time, right? Unfortunately, this is not the case, and whilst neural nets are a great step in the right direction, they are really only a piece of the puzzle that is human language.

It is no stretch of the imagination to see how this technology would be effective in helping computers better understand and mimic human language. Given enough examples, a computer is able to form a structure that can take a previously unseen input and produce a best guess output based off of the relationships it has formed in its training stage. These network paths, much like the neural networks found in the human brain, strengthen and wane as the computer tries to develop probability-weighted associations between the provided input and desired output. Neural networks are a form of artificial intelligence that rely on the computer learning from large batches of data. To first understand the role of a transformer in tackling human language, we must understand a little bit about deep learning and neural networks.
WHAT DOES TRANSFORMER EN MEAN IN FRENCH FULL
Much like the language we aim to teach computers to understand, the NLP field is full of jargon, semantic terms, and many layers of complicated topics and ideas. RNNs and the problem with Sequence Learning Over the course of this article, I will explore some of the key topics you’ll need to understand transformers, the current state of NLP, and Google’s breakthrough transformer BERT. One new technique that has helped accelerate NLP is the application of what is called a transformer. Image credit: NLP & DL (winter 2017) Stanford Understanding language can be a difficult task, many models have different strategies to achieve this goal. Because of this difficulty, the field is constantly looking for new techniques and innovations to help machines tackle language and human communication. Unfortunately for NLP specialists, human language, be it English or Mandarin, is complicated, messy, and regularly changing, making it very challenging to translate to machines. Technologies such as spam detection, predictive text, virtual assistants, search engines, sentiment analysis, and translators are but a few examples of the plethora of applications for NLP that have become staples in our world. However, its application and importance in our world is undeniable. To the untrained eye, NLP may not seem like an important or relatively difficult task. Born out of a combination of linguistics, mathematics, and computer science, NLP is the exploration of drawing data, meaning, and understanding from the swaths of text data in our world.
Because of the nature of data science, many of these topics span different disciplines or even make up their own disciplines such as the field of natural language processing or NLP. Natural Language Processing?Īs an undergraduate data scientist, I am often exposed to a range of new topics and ideas shaping the world of data science. Pictured: Bert (right) and Ernie (left) from the popular children’s show Sesame Street.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
